Biological timing: Linking the circadian clock to the season
03/01/2023The circadian clock is thought to provide the internal time reference for measuring day length, allowing organisms to prepare in advance for the coming winter and summer. A new study sheds light on the neural link between the circadian clock and seasonal timing.
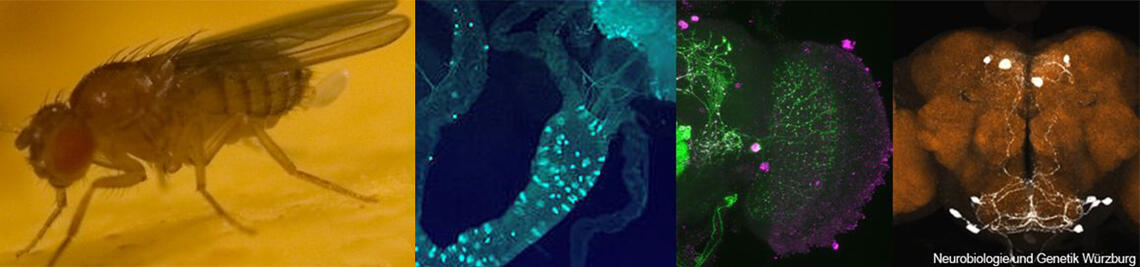
Organisms living in temperate zones are exposed to prominent seasonal changes which they need to prepare for in advance. Failure to prepare for winter will ultimately result in death. Conversely, failure to prepare for reproduction in spring will result in no offspring. Most animals time reproduction to spring and summer and some of them shrink their gonads in autumn and winter. This happens also in small insects such as fruit flies that enter reproductive arrest, also called dormancy. They shrink their gonads and drastically reduce their metabolism. Additionally, they increase stress resistance and their nutrient reservoir before the winter sets in1. Dormant flies can survive the entire winter without feeding and reproducing. As soon as spring sets in, they terminate dormancy and start feeding and reproducing again.
Journal: Current Biology
Author: Professor Charlotte Helfrich-Förster
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2023.01.026