mRNA decay
mRNA decay (Kramer lab)
mRNA decay
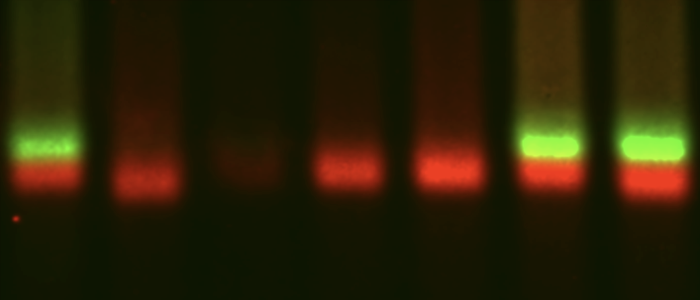
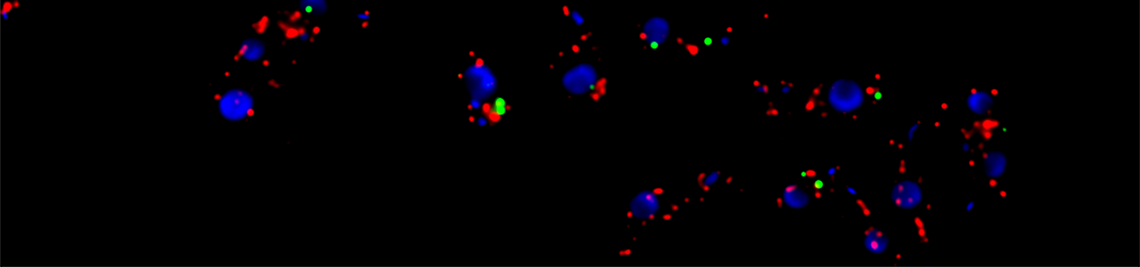
Trypanosomes use an ApaH-like phosphatase for mRNAs decapping
mRNA decapping is the critical step in 5’-3’ mRNA decay. Usually, a nudix domain protein (the prototype is Dcp2) hydrolyses the phosphate bound of the mRNA cap between the alpha and beta phosphate and produces monophosphorylated RNAs, which become a substrate for an exoribonuclease. Trypanosomes have a highly unusual cap structure that is heavily methylated at the first four transcribed nucleotides (cap4). This could be the reason why they do not have a homologue to Dcp2. Instead, we recently round that the parasites use an ApaH-like phosphatase as their major decapping enzyme. The further characterisation of this enzyme is a core focus of the Kramer lab. ALPH1 is the first non-nudix- domain decapping enzyme and it is already clear that the decapping mechanism is very different: cleavage does not take place between the alpha and beta phosphate. Furthermore, ApaH-like phosphatases, which originate from bacteria, are present in a patchy way throughout all the eukaryotic super-groups, but no enzyme has yet been functionally characterised. It is very tempting to speculate that ApaH like phosphatases also act in mRNA decapping in other eukaryotes.
Publications
Bannerman, B. P., Kramer, S., Dorrell, R. G., & Carrington, M. (2018). Multispecies reconstructions uncover widespread conservation, and lineage-specific elaborations in eukaryotic mRNA metabolism. PLoS ONE, 13(3), e0192633–23.
Kramer S. 2017. The ApaH-like phosphatase ALPH1 is the major mRNA decapping enzyme of trypanosomes. PLoS Pathog. 13:e1006456.
Kramer S. 2017. Simultaneous detection of mRNA transcription and decay intermediates by dual colour single mRNA FISH on subcellular resolution.Nucleic Acids Res 45:e49.
Kramer S, Piper S, Estevez A, Carrington M. 2016. Polycistronic trypanosome mRNAs are a target for the exosome. Mol Biochem Parasitol205:1–5.
Kramer S, Carrington M. 2014. An AU-rich instability element in the 3’UTR mediates an increase in mRNA stability in response to expression of a dhh1 ATPase mutant.Translation 2: e28587
Kramer S, Queiroz R, Ellis L, Hoheisel JD, Clayton C, Carrington M. 2010. The RNA helicase DHH1 is central to the correct expression of many developmentally regulated mRNAs in trypanosomes.J Cell Sci 123: 699-711.
Kramer S, Queiroz R, Ellis L, Webb H, Hoheisel JD, Clayton C, Carrington M. 2008. Heat shock causes a decrease in polysomes and the appearance of stress granules in trypanosomes independently of eIF2(alpha) phosphorylation at Thr169.J Cell Sci 121: 3002-3014.